Palette Layout & Coloring
Customize the layout, chord filter and dynamic coloring of a Standard Palette or Alternative Palette to help you explore new paths to building chord progressions.
Layout
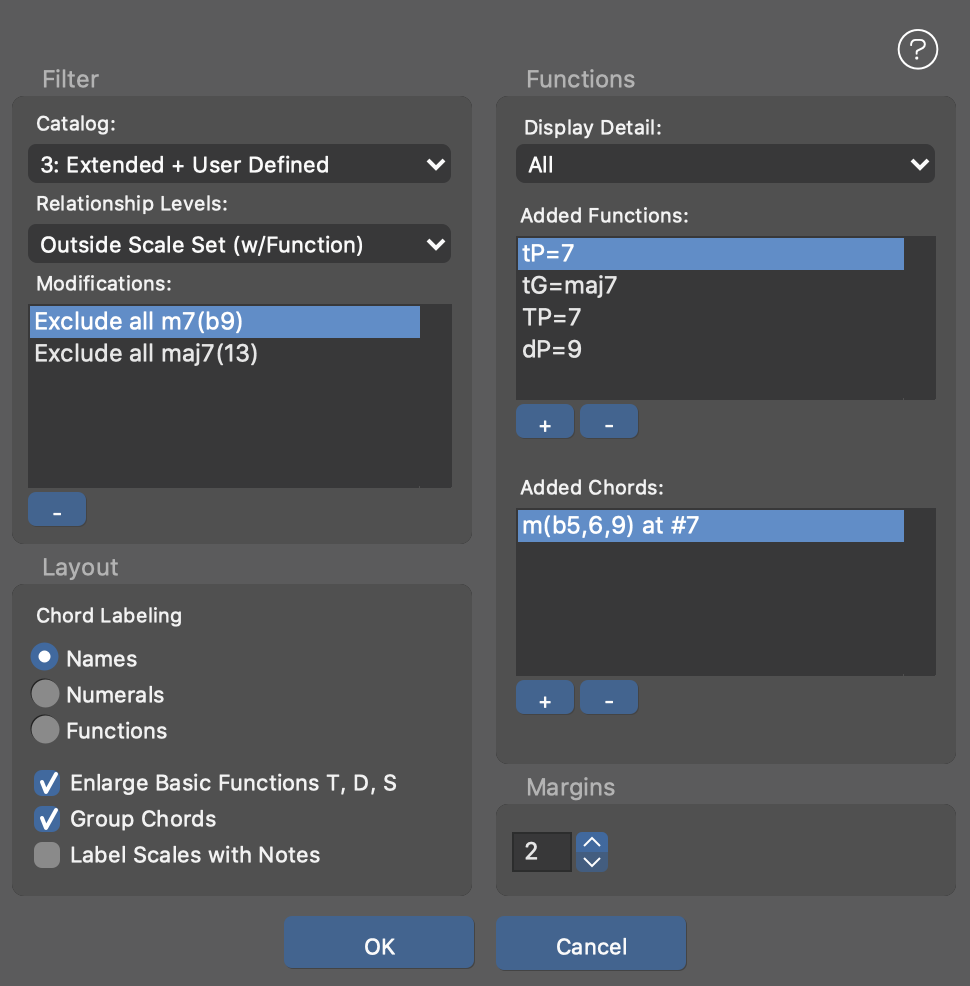
Edit the chord filter and layout options with . Make all possible chords appear in a layout with . With you can restore the default layout.
Chord Filter Settings
- Catalog
- Select a level of detail: Basic Chords Only, Standard, Extended or Extended + User Defined.
- Relationship Levels
- Minimum grade of relationship for a chord to show up:
- Modifications
- A list of options you have set for individual chords from the right-click menu over a chord. This list is for information and selectively deleting options.
- Functions (Display Detail)
- Level of detail for harmonic function labels.
- Added Functions
-
Add arbitrary harmonic functions to the palette, typed as function expressions or as a chord.
- Added Chords
- Add arbitrary chords that do not appear in the palette by default, like more remotely related functions. If Synfire recognizes the chord as a valid harmonic function, it will be added to the Added Functions list.
- Layout
-
Other layout settings
-
Names, Numerals or Functions Determines the way in which chord names are displayed. In Function mode, chords that have no significant function are filtered out, reducing the number of chords significantly.
-
Enlarge Basic Functions T, D, S Emphasizes the primary functions Tonic (T), Sub-dominant (S), and Dominant (D) by enlarging the chord boxes.
-
Group Chords Similar chords are grouped into a common box. Greatly improves clarity.
-
Label Scales With Notes Note names are used to label the center line instead of Roman numerals.
-
- Margins
- The margins between boxes.
Including And Excluding Chords
Besides using the layout settings dialog, there are more ways to include chords with a palette, or exclude (hide) them.
- Including Chords
-
-
Add a chord by name or function as described above.
-
Drop a chord on the palette from another palette or progression.
-
To show chords that have previously been hidden, select any chord at the desired scale degree and choose or from the right-click menu respectively.
-
Use to include all chords of the current progression on the clipboard.
-
- Excluding Chords
-
Hide all chords that you find unnecessary, distracting or can't play.
-
Select one or more chords in the palette and hide them with .
-
Hide all chords of a particular type with .
-
- Marking Chords
-
Highlight chords with a color band, so you can better remember them, or to draw the attention of others to a distinctive spot on your palette.
-
Select the desired chords in the palette and use the menu to add or remove color markings.
-
To mark all chords of a the same type, hold down ⇧ Shift when picking the above mentioned menu item.
-
Use to mark all chords of the current progression on the clipboard.
-
Coloring Settings
The current Coloring Scheme of a Palette can be examined and edited with . Several built-in coloring algorithms can be placed in a sequence to compute the final color of a chord from the top down.
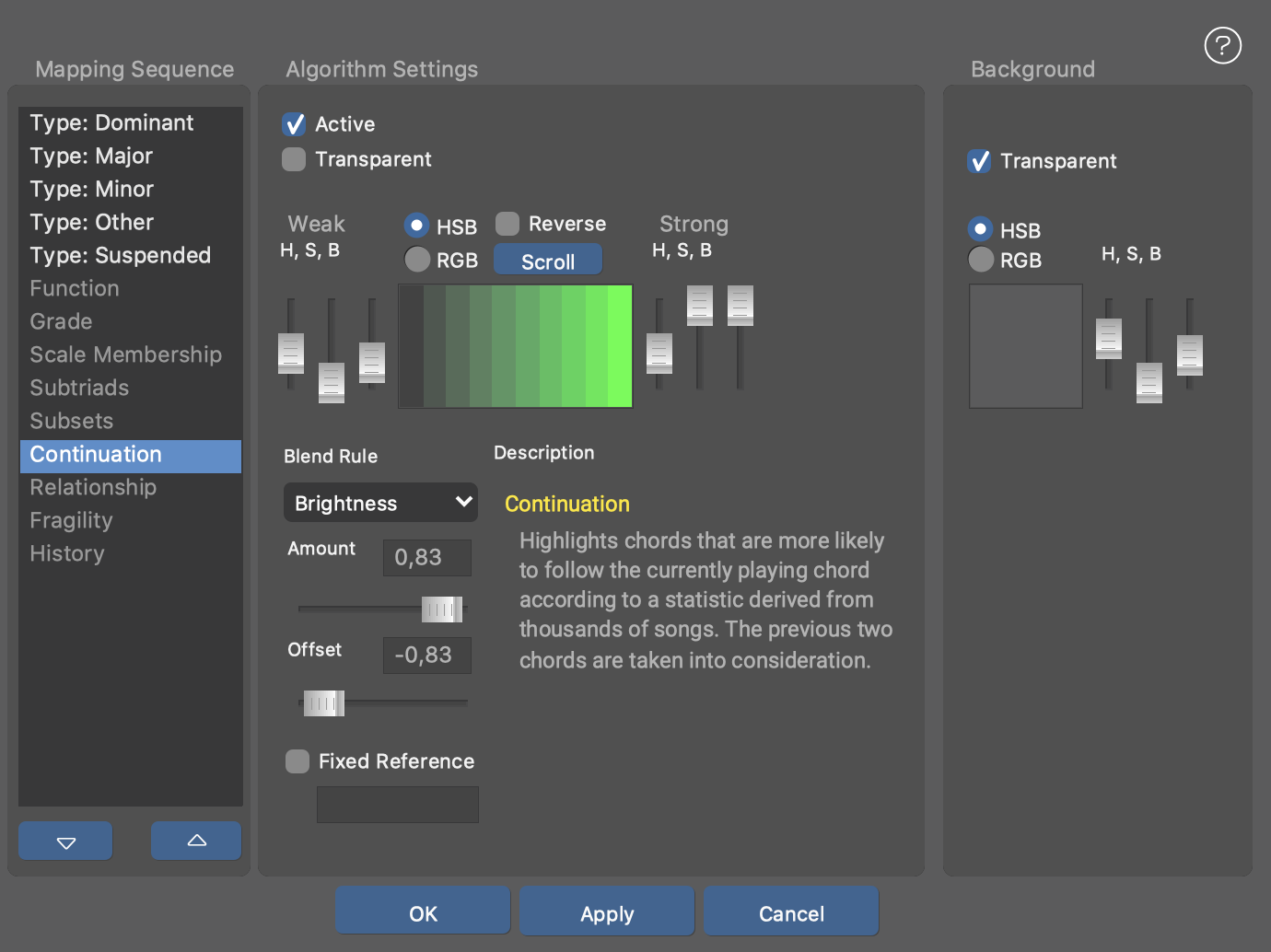
- Mapping Sequence
- Select an algorithm. Use the up and down buttons below the list to change the position of an algorithm in the sequence. Color is computed from the top down, each algorithm processing the color of the previous one.
- Active
- Enables the selected algorithm. A disabled algorithm is bypassed.
- Transparent
- Makes the previous color pass through unchanged where the algorithm delivers an undefined value.
- Color Gradient Settings
- Defines how values
0.0 … 1.0are mapped to a color. Select RGB or HSB color space and set the beginning and end values of the gradient. Use Reverse to reverse the gradient and Scroll to rotate it. - Amount, Offset
- Multiplies the value of the algorithm by an Amount and adds an Offset to it, before it is mapped to the color gradient. Not all blend rules make use of these settings.
- Blend Rule
-
Determines how the color of the previous algorithm is combined with the color of the current one.
-
Blend: Blend both colors in a ratio set by the Amount slider.
-
Brightness: Modulate the brightness of the previous color, using the Amount and Offset sliders.
-
Saturation: Modulate the saturation of the previous color, using the Amount and Offset sliders.
-
Hue: Modulate the color hue of the previous color, using the Amount and Offset sliders.
-
Replace: Replace the previous color with the current, unless it is undefined.
-
- Fixed Reference
-
Defines a particular chord as the permanent input to the coloring scheme. That is, the coloring stays put and won't follow the chords being clicked. Select the desired chord in the palette before you open the dialog and enable this setting.
Tip: Fixed Reference is a way to permanently freeze a coloring you happen to find useful.
Coloring Algorithms
The menu can be used to enable or disable any of the built-in coloring algorithms, all of which are listed below.
Static Coloring
These coloring algorithms provide useful background shading for orientation and don't update with a new chord.
- Type: Suspended
- Highlights suspended chords with shades of green.
- Type: Dominant
- Highlights dominant chords with shades of red.
- Type: Major
- Highlights major chords with shades of yellow.
- Type: Minor
- Highlights minor chords with shades of blue.
- Type: Other
- Highlights other chord types with shades of cyan.
- Function
- Highlights chords with a strong functional significance. Primary functions Tonic, Sub-dominant, and Dominant are considered strong. Secondary functions appear dimmed. Chords lacking a clear function remain dark. This scheme provides orientation, especially in Alternative Palettes with an unfamiliar structure.
- Grade
- Indicates the grade of relationship a chord has to the Scale Set of the palette. The brighter a chord, the closer its relationship to the reference scale.
- Scale Membership
- Each scale of the Scale Set is associated with a color. A chord shows up in a color only if it can be built exclusively from the notes of the associated scale (and no notes from other scales). This highlights all chords that may best emphasize the characteristics of a particular scale.
Dynamic Coloring
These coloring algorithms highlight some relationship with the chord currently playing.
- Sub-triads
- Highlights all simple triads that are completely contained in the currently played chord. You can play these triads as simplified substitutes for the current chord, or achieve polytonality by letting multiple instruments each play a different sub-triad using the Layer parameter.
- Subsets
- Highlights all chords that are completely contained in the chord currently being played. This allows you to find several smaller chords that would make up the current chord if played together.
- Supersets
- Highlights all chords that contain the current chord in full. This allows you to find more complex chords that are suitable as an extension to the current chord.
- Intersection
- Highlight appears brighter the more notes a chord has in common with the currently playing chord. If you click along a path of brighter chords, the sound will only change gradually. Conversely, you can achieve a stronger contrast by following a path along darker chords.
- Relationship
- Highlights chords whose harmonic function is closer to the function of the currently playing chord.
- Strength
- Highlights chords that, when played next, introduce a strong change from the currently playing chord. A short distance in the circle of fifths is considered strong. Longer distances are considered weaker. For example, you could follow the bright path for a chorus and the dark path for a verse.
- Continuation
- Highlights chords that are more likely to follow the currently playing chord according to a statistic derived from thousands of songs. The previous two chords are taken into consideration.
- History
- Highlights the recently visited chords as a slowly fading trail of green color to help you remember what you were playing.
- Tonnetz
- Chords related to the current chord are highlighted according to the Tonnetz (Tone Network) theory. Neighbors S, N, L, R, P each show a distinct color. Learn more about the Tonnetz on Wikipedia.
Saving Presets For Layouts
You can save a layout as a preset with . Presets you saved to the folder Layouts in the Configuration Folder will appear in the preset menu.
Saving Presets For Coloring Schemes
Save a coloring scheme as a preset with . Presets you saved to the folder Colorings in the Configuration Folder will appear in the preset menu.